 I. Foundational Architecture: Engineered Fusion Protein Design
I. Foundational Architecture: Engineered Fusion Protein Design
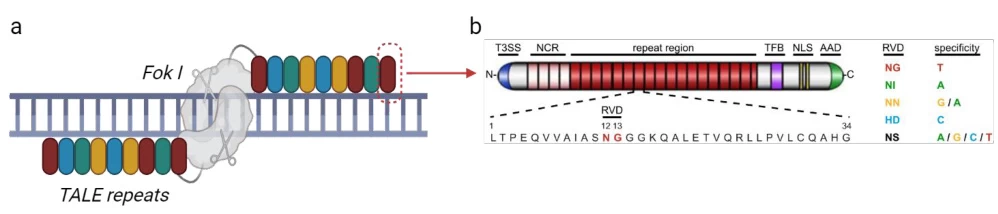
TALENs (Transcription Activator-Like Effector Nucleases) are synthetic proteins engineered by fusing two functional domains:
- DNA-Binding Domain: Derived from Xanthomonas bacterial TALE proteins
- Cleavage Domain: FokI endonuclease for targeted DNA scission
(Fig. 1: TALEN Structural Blueprint)
Description: Modular architecture showing N-terminal T3S signal (yellow), central repeat domain (multicolored), C-terminal nuclear localization signal (blue), and FokI nuclease (red). DNA strand with target sequence highlighted.
II. Core Recognition System: The RVD Code
The TALEN specificity relies on Repeat-Variable Diresidues (RVDs) within each 33-35 amino acid repeat :
| RVD Code | Target Base | Binding Affinity |
|---|---|---|
| HD | C | High specificity |
| NI | A | High specificity |
| NG | T | Moderate specificity |
| NN | G/A | Broad recognition |
| Each RVD recognizes a single nucleotide through direct hydrogen bonding |
(Fig. 2: RVD-DNA Interaction)
Description: Molecular model showing HD RVD (green) forming hydrogen bonds (dashed lines) with cytosine (blue) in DNA major groove.
III. DNA Cleavage Dynamics: Dimerization-Driven Scission
TALENs operate as obligate dimers for precise cleavage :
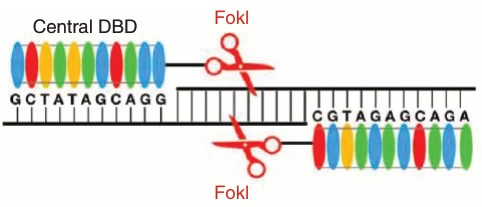
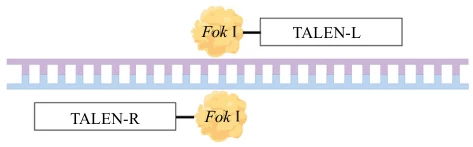
- Target Site Selection: Two TALENs bind opposing DNA strands flanking a 12-24 bp spacer
- FokI Dimerization: Nucleases form active dimer only upon correct spacing
- Double-Strand Break (DSB): Dimeric FokI cleaves DNA creating 5′ overhangs
(Fig. 3: Cleavage Mechanism)
Description: TALEN-L (left) and TALEN-R (right) bound to DNA. FokI domains dimerize across spacer region inducing DSB.
IV. Engineering Workflow: From Design to Validation
A. Modular Assembly Pipeline
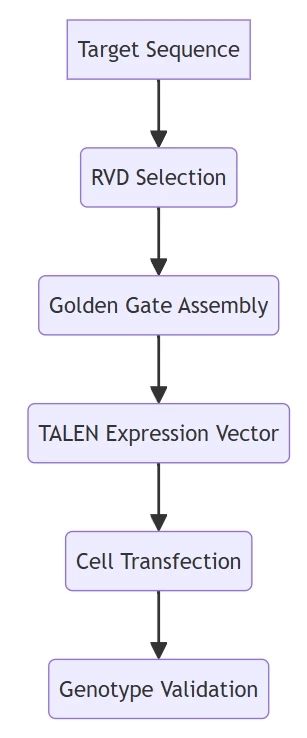
Based on high-efficiency cloning systems
B. Design Parameters
| Parameter | Requirement | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Spacer Length | 12-24 bp | Optimal FokI dimerization |
| 5′ Base Preference | T at position 0 | Enhanced binding efficiency |
| Repeat Number | 15-20 units | Balance specificity/expression |
V. Unique Advantages in Genome Editing
A. Chromatin Accessibility
TALENs outperform CRISPR in heterochromatic regions due to:
- Helix-Sliding Mechanism: Navigates nucleosome-packed DNA
- Methylation Resistance: Unaffected by CpG methylation
B. Precision Metrics
| Parameter | TALEN | CRISPR-Cas9 |
|---|---|---|
| Off-Target Rate | 0.1-0.5% | 1-10% |
| PAM Requirement | None | Essential (e.g., 5′-NGG-3′) |
| GC-Rich Targets | Efficient | Challenging |
VI. Therapeutic & Agricultural Applications
A. Clinical Breakthroughs
- SCID-X1 Therapy: IL2RG correction in hematopoietic stem cells
- Hepatitis B Cure: cccDNA cleavage in infected hepatocytes
B. Agricultural Innovations
(Fig. 4: Calyxt High-Oleic Soybean)
Description: Field trial results showing 80% oleic acid content in TALEN-edited soybeans versus 20% in wild-type
Conclusion: The Precision Specialist
TALEN technology delivers unparalleled editing precision through:
- Programmable Specificity: RVD code enables base-resolution targeting
- Context Flexibility: Chromatin accessibility without PAM constraints
- Clinical-Grade Safety: Low off-target rates in therapeutic applications
“Where CRISPR democratizes gene editing, TALEN perfects it—offering surgical precision where others see molecular barriers.”
— Nature Biotechnology, 2025
Future development focuses on AI-optimized RVD design (2026) and single-molecule delivery systems (2028) to enhance in vivo efficiency.
Data sourced from publicly available references. For collaboration or domain acquisition inquiries, contact: chuanchuan810@gmail.com.
