RNA-Mediated Feedback Regulation of DNA Activities: Molecular Mechanisms and Biological Significance
An Integrated Analysis with Regulatory Pathway Visualizations
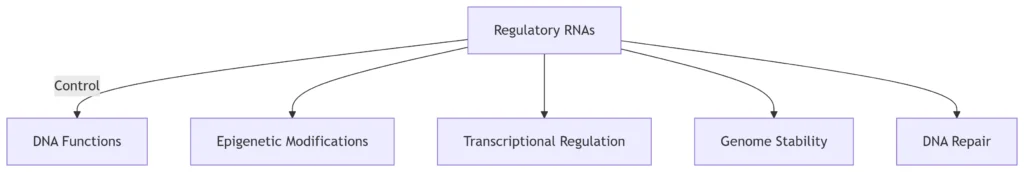
1. RNA Interference (RNAi) Pathway: Transcriptional Silencing
Mechanism:

-
Key Components:
-
siRNA: Targets complementary genomic loci
-
Argonaute 4 (AGO4): Recruits DNA methyltransferases
-
H3K9me: Histone methylation mark for heterochromatin formation
-
-
Biological Example:
Arabidopsis transposon silencing via 24-nt siRNAs
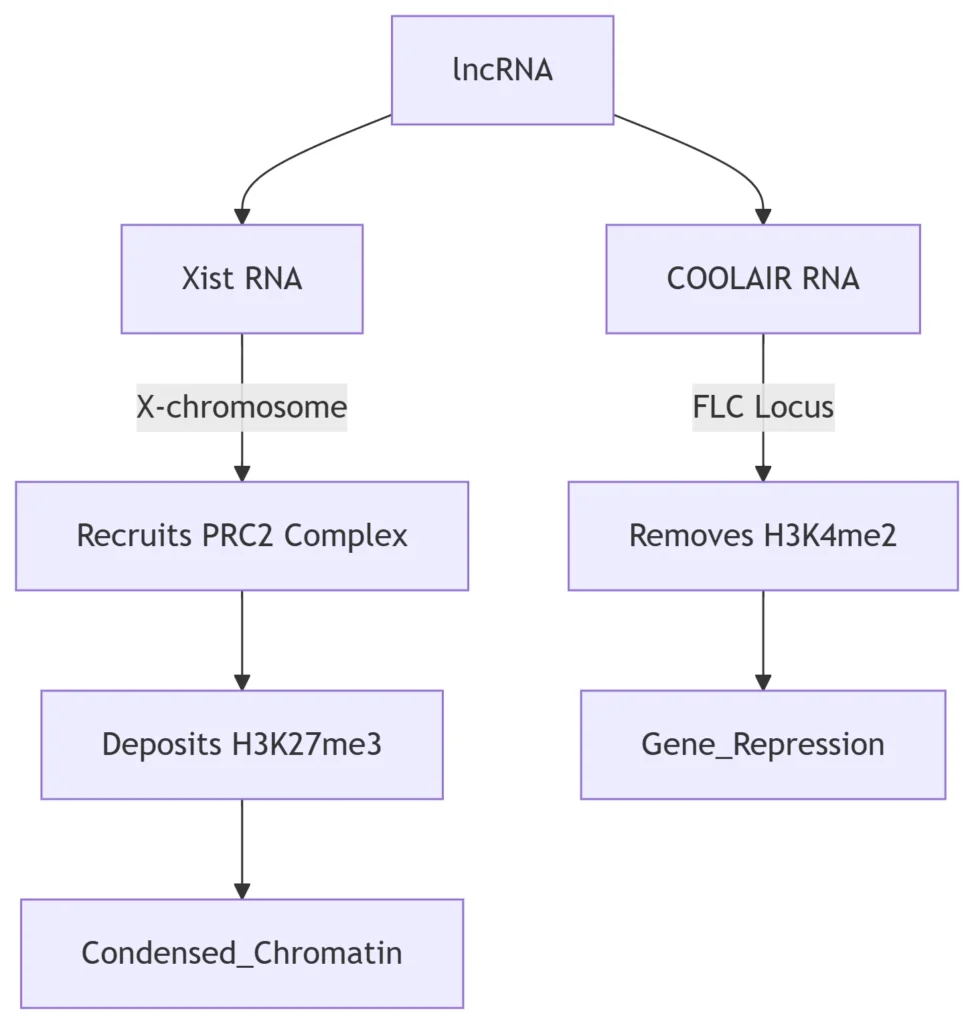
2. Long Non-Coding RNA (lncRNA) Mediated Regulation
Chromatin Remodeling Mechanisms:
-
Functional Impact:
-
Xist: Inactivates one X chromosome in females (dosage compensation)
-
COOLAIR: Represses FLOWERING LOCUS C in vernalization
-
TERRA: Regulates telomere length and stability
-
3. RNA-Directed DNA Repair
Homology-Directed Repair (HDR):

-
Experimental Evidence:
-
RNA-templated repair in yeast and human cells (Nature, 2020)
-
RNA-guided DNA repair efficiency: ~30% of HDR events
-
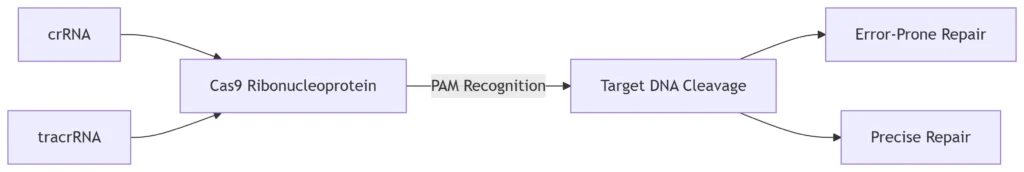
4. CRISPR-Cas Systems: Adaptive Immunity
Type II CRISPR-Cas9 Mechanism:
-
Feedback Regulation:
-
crRNA generation from viral DNA spacers
-
Auto-regulatory RNA elements control cas gene expression
-
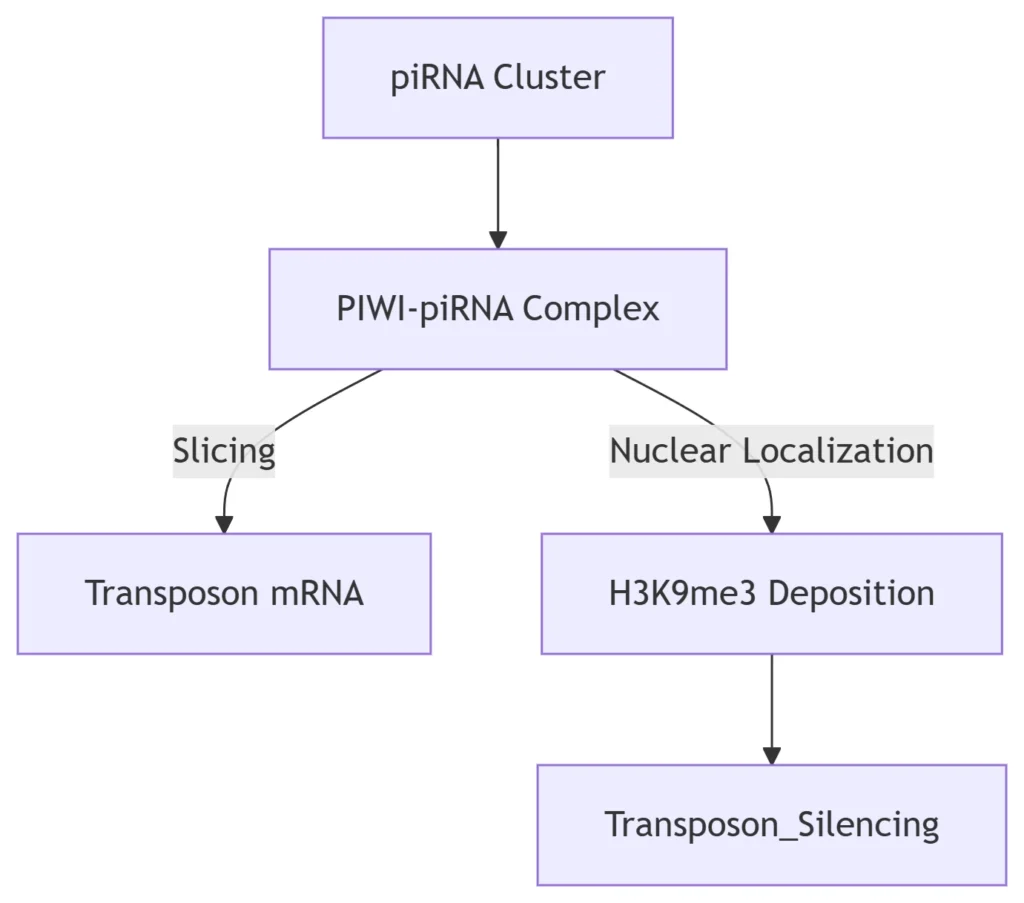
5. Retrotransposon Control via piRNAs
piRNA Pathway in Germline:
-
Key Features:
-
24-31 nt piRNAs derived from antisense transcripts
-
“Ping-pong” amplification cycle in Drosophila
-
6. RNA-Mediated Epigenetic Memory
Paramutation Mechanisms:

-
Plant Model Systems:
-
Zea mays b1 locus paramutation
-
Transgenerational inheritance for ≥10 generations
-
7. Quantitative Regulatory Impact
| RNA Type | Target DNA Process | Regulation Efficiency | Biological Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| siRNA | DNA methylation | 70-90% TEs silenced | Genome stability |
| lncRNA | Chromatin conformation | 2-5 fold gene repression | Cellular differentiation |
| piRNA | Transposon suppression | 99% germline protection | Fertility maintenance |
| dRNA | DNA repair | 30% HDR enhancement | Mutagenesis prevention |
| CRISPR RNA | Viral DNA cleavage | >95% target elimination | Adaptive immunity |
Biological Significance
-
Developmental Programming:
-
Xist-mediated XCI ensures proper embryogenesis
-
Plant lncRNAs regulate flowering time and stress responses
-
-
Disease Connections:
-
piRNA dysfunction → male infertility (azoospermia)
-
Xist misregulation → autoimmune disorders (e.g., lupus)
-
-
Evolutionary Adaptation:
-
CRISPR systems provide prokaryotic antiviral defense
-
RNA-mediated TE control shapes genome architecture
-
Therapeutic Applications
Conclusion
RNA serves as a master regulator of DNA activities through diverse feedback mechanisms:
-
Epigenetic Control: RNA-directed DNA methylation and histone modifications
-
Structural Regulation: lncRNA-mediated chromatin looping and compartmentalization
-
Genome Defense: RNA-guided antiviral systems and transposon silencing
-
Repair Guidance: RNA-templated DNA damage correction
These RNA-DNA interactions create dynamic regulatory circuits enabling adaptive responses to environmental challenges, developmental cues, and genomic threats. The programmable nature of RNA-mediated DNA targeting (CRISPR, RNAi) has revolutionized biotechnology, offering precise tools for gene therapy and synthetic biology.
Data sourced from public references including:
-
Holoch D. & Moazed D. Nature Reviews Genetics (2015)
-
Mattick J.S. Cell (2023)
-
NRA Database (Non-coding RNA Atlas)
-
ENCODE Project Consortium
For research collaboration or content inquiries: chuanchuan810@gmail.com
