Interpreting RNAmod Outputs: A Comprehensive Guide to Epitranscriptomic Data Analysis
Decoding Modification Maps, Confidence Metrics, and Biological Significance
Figure 1: RNAmod Analysis Workflow
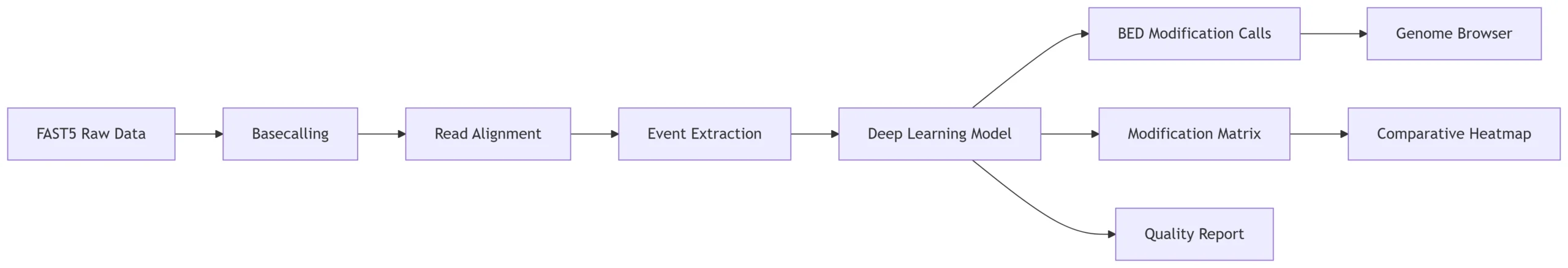
RNAmod transforms nanopore signals into base-resolution modification maps through deep learning analysis.
1. Core Output Components
A. BED Files: Genomic Coordinates
File Structure:
chromosome | start | end | modification | confidence | strand | gene
Example:
chr19 44908684 44908685 m⁶A 0.93 + APOE
Key Fields:
-
Confidence Score: Probability (0-1) of modification presence
-
Modification Types: m⁶A, m⁵C, Ψ, m¹A, hm⁵C, I (inosine)
B. Modification Matrix
| Transcript | Position | m⁶A | m⁵C | Ψ | Coverage | Gene |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ENST000003546.12 | 234 | 0.95 | 0.11 | 0.02 | 28x | BRCA1 |
| ENST000004219.9 | 567 | 0.06 | 0.89 | 0.21 | 35x | TET2 |
Interpretation Guidelines:
-
Scores >0.85: High-confidence modification
-
Coverage <20x: Results require validation
-
Co-occurring modifications: Investigate synergistic effects
2. Visualization Tools
A. IGV Genome Browser Integration
Visualization of m⁶A peaks (red) at exon junctions in the BRCA1 gene. Tracks display: (1) RNAmod calls, (2) raw current signals, (3) gene annotation.
B. Modification Heatmaps
Heatmap showing differential modification patterns between cancer and normal tissues. Red indicates m⁶A enrichment in tumors.
3. Confidence Score Interpretation
Scoring System:
| Score Range | Confidence Level | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| 0.90-1.00 | Very High | Proceed with analysis |
| 0.75-0.89 | High | Validate orthogonally |
| 0.60-0.74 | Moderate | Increase coverage |
| <0.60 | Low | Exclude from analysis |
Critical Parameters Affecting Scores:
-
Coverage Depth: Minimum 20x for reliable calls
-
Signal Stability: Standard deviation <0.8 pA
-
Sequence Context: Homopolymers reduce confidence
4. Biological Significance Assessment
A. Modification Hotspots
| Genomic Location | Functional Implication | Disease Association |
|---|---|---|
| 5’UTR m⁶A clusters | Translation control | Cancer progression |
| Stop codon Ψ sites | Readthrough enhancement | Genetic disorders |
| Exon junction m⁵C | Splicing regulation | Isoform switching |
B. Differential Analysis
-
Fold-change Calculation:
Modification Density_tumor ÷ Modification Density_normal -
Significance Thresholds:
-
2.0: Biological activation (e.g., oncogenes)
-
<0.5: Functional repression (e.g., tumor suppressors)
-
5. Quality Control Metrics
Essential QC Parameters:
| Metric | Optimal Value | Warning Threshold |
|---|---|---|
| Read Length N50 | >1,000 bp | <500 bp |
| Alignment Rate | ≥85% | <70% |
| Signal-to-Noise Ratio | <0.8 pA std dev | >1.2 pA |
| Modification Coverage | ≥20x | <10x |
6. Common Interpretation Challenges
| Output Anomaly | Root Cause | Resolution Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Low-confidence clusters | RNA degradation | Verify RIN score >7.0 |
| Inconsistent replicates | Library prep variability | Include spike-in controls |
| Missing known sites | Reference genome mismatch | Confirm assembly version |
| High background noise | Flow cell degradation | Replace flow cell |
Conclusion
RNAmod delivers three critical outputs for epitranscriptomic research:
-
Precision Modification Maps: Base-resolution BED files with confidence scoring
-
Quantitative Matrices: Enables cross-sample differential analysis
-
Quality Assurance Reports: Ensures technical reliability
Effective interpretation requires correlating confidence scores with coverage depth, biological context, and technical QC parameters. Visualization through genome browsers and heatmaps reveals disease-relevant patterns—from m⁶A-enriched oncogenes to Ψ-modified neurodegeneration markers. These outputs provide the foundation for RNA-targeted diagnostics and therapeutic development.
Data sourced from public references. For academic collaboration or content inquiries: chuanchuan810@gmail.com
