DNA and RNA in Genetic Information Transfer: Molecular Orchestrators of Heredity
A Comprehensive Analysis of Their Complementary Roles
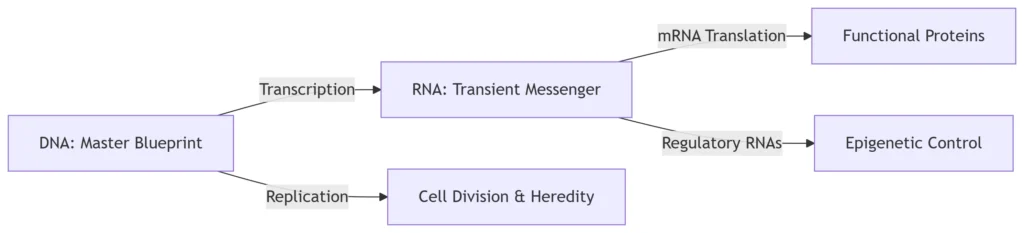
1. DNA: The Archival Repository
Core Functions:
-
Genetic Storage: Encodes hereditary information in nucleotide sequences (A/T/C/G)
-
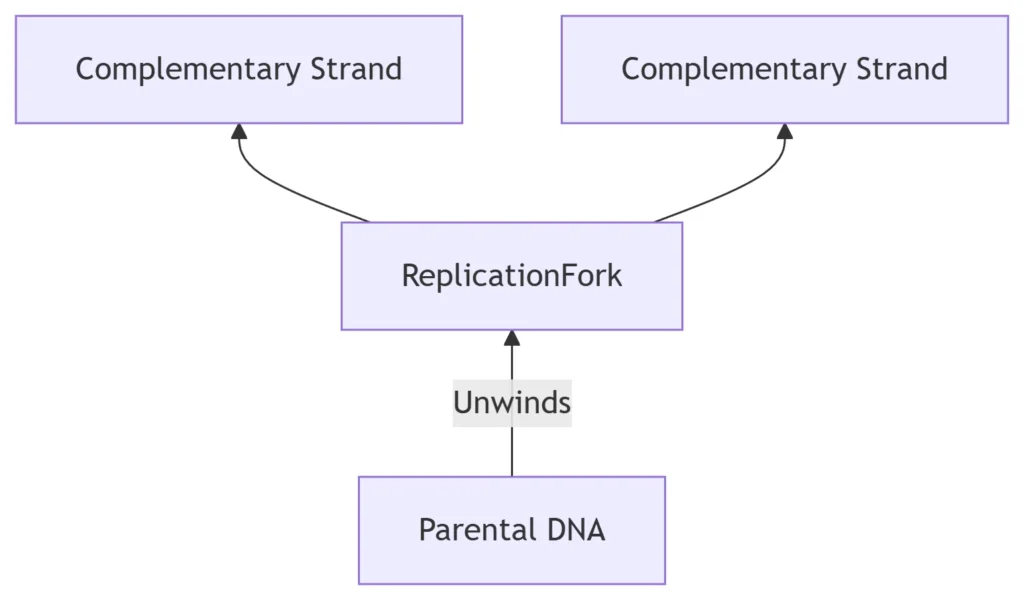
Replication Template: Semi-conservative duplication via DNA polymerase
Key Mechanism:
-
Antiparallel Synthesis: Leading (5’→3′) and lagging strands (Okazaki fragments)
-
Error Correction: Proofreading (3’→5′ exonuclease) maintains <10⁻⁹ error rate
2. RNA: The Dynamic Executor
Information Flow Pathways:
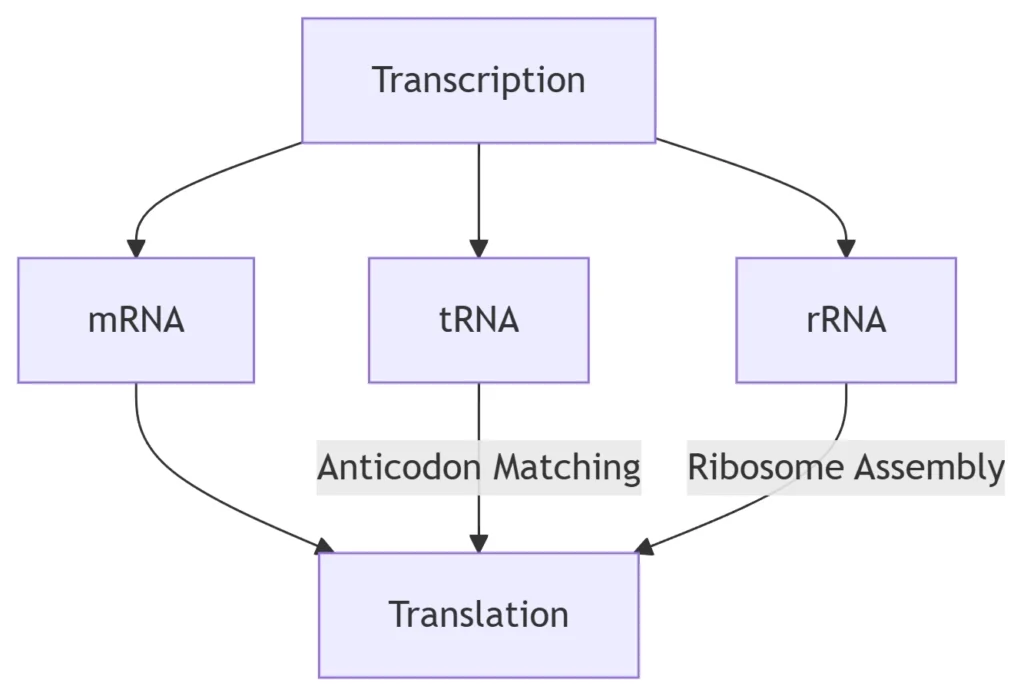
RNA Functional Classes:
RNA Type Role in Information Transfer Molecular Mechanism mRNA Encodes polypeptide sequences Codon-anticodon recognition at ribosomes tRNA Translates codons to amino acids Charged with aa by aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases rRNA Catalyzes peptide bond formation 23S rRNA ribozyme activity (prokaryotes) miRNA/siRNA Post-transcriptional gene silencing RISC complex-mediated mRNA degradation
3. Integrated Workflow: Central Dogma in Action
Step 1: Transcription Initiation

-
Key Features:
-
Template strand: 3’→5′ direction
-
mRNA synthesis: 5’→3′ elongation (NTPs polymerization)
-
Step 2: RNA Processing
-
Eukaryotic Modifications:
-
5′ capping (7-methylguanosine)
-
3′ polyadenylation (200+ adenines)
-
Splicing (snRNP-mediated intron removal)
-
Step 3: Translation

-
Decoding Process:
-
P-site: Holds growing polypeptide
-
A-site: Accepts incoming tRNA
-
E-site: Empty tRNA exit
-
4. Specialized Information Transfer Systems
Mitochondrial Genome:
-
mtDNA: Circular DNA encoding 13 OXPHOS proteins
-
Mitochondrial RNA: Dedicated transcription/translation machinery
Viral Subversion Strategies:
Virus Type Information Flow Example Retroviruses RNA → DNA (Reverse transcription) HIV RNA Viruses Direct RNA replication SARS-CoV-2 DNA Viruses Host-dependent transcription Herpes simplex
5. Regulatory Hierarchies
Epigenetic Control:
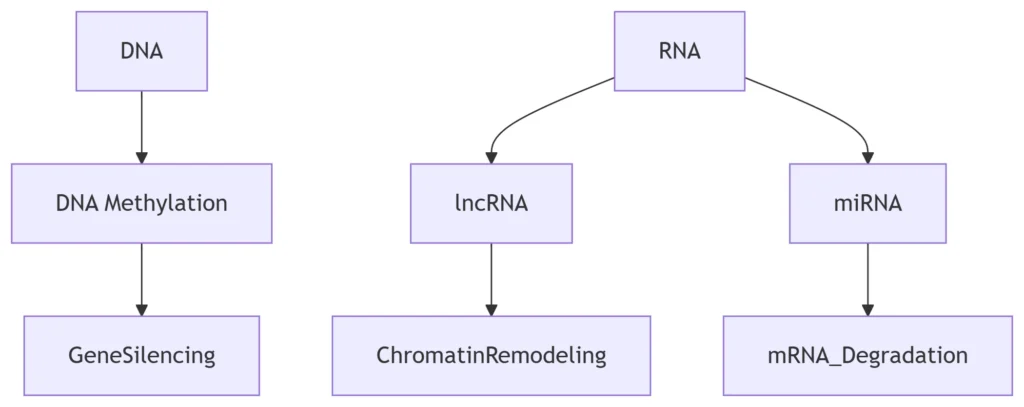
-
Cross-Talk Mechanisms:
-
RNA-directed DNA methylation (RdDM) in plants
-
Xist lncRNA-mediated X-chromosome inactivation
-
6. Quantitative Information Metrics
Parameter DNA RNA Information Density ~3 GB/human genome Transient copies (minutes-hours) Transcription Rate 25-60 nt/sec (eukaryotes) N/A Translation Rate N/A 6-9 aa/sec (eukaryotes) Error Frequency 1/10⁹ bases (replication) 1/10⁴ bases (transcription)
7. Evolutionary Perspectives
-
RNA World Hypothesis: Self-replicating RNA predated DNA-protein systems
-
Molecular Fossils: Ribosomal RNA conservation across taxa (universal phylogeny)
-
Viral Origins: Retroviral reverse transcriptase links RNA/DNA worlds
Conclusion
DNA serves as life’s permanent information archive, enabling precise hereditary transmission through semi-conservative replication. RNA functions as the versatile information conduit, dynamically converting genetic blueprints into functional molecules via transcription, translation, and regulatory networks. Their symbiotic relationship—DNA providing stability and fidelity, RNA enabling adaptability and expression—forms the cornerstone of molecular genetics. Modern biotechnologies (CRISPR, mRNA vaccines) exploit these natural roles to revolutionize medicine and synthetic biology.
Data sourced from public references including:
-
Alberts B. et al. Molecular Biology of the Cell (7th ed.)
-
Lodish H. et al. Molecular Cell Biology (9th ed.)
-
NCBI Gene Database & RCSB PDB
For research collaboration or content inquiries: chuanchuan810@gmail.com
-
