A Technical Guide for Robust Epitranscriptomic Analysis
Figure 1: RNAmod Workflow with Error-Prone Stages

Red-highlighted stages represent high-error frequency zones.
1. Sample Preparation Errors
A. RNA Degradation
-
Symptoms:
-
Bioanalyzer RIN <7.0
-
Truncated reads (N50 <500 bp)
-
High 18S/28S ratio in electropherograms
-
-
Root Causes:
-
Repeated freeze-thaw cycles
-
RNase contamination during extraction
-
-
Solutions:
-
Aliquot RNA after single freeze
-
Use RNaseZap-treated surfaces
-
B. Insufficient Input Material
-
Consequences:
-
Coverage <10x at critical sites
-
False-negative modification calls
-
-
Remediation:
Sample Type Minimum Input Compensation Strategy Cell Lines 50 ng SPRI bead size selection Tissues 100 ng SMART-seq amplification
2. Library Construction Pitfalls
A. Adapter Dimer Formation
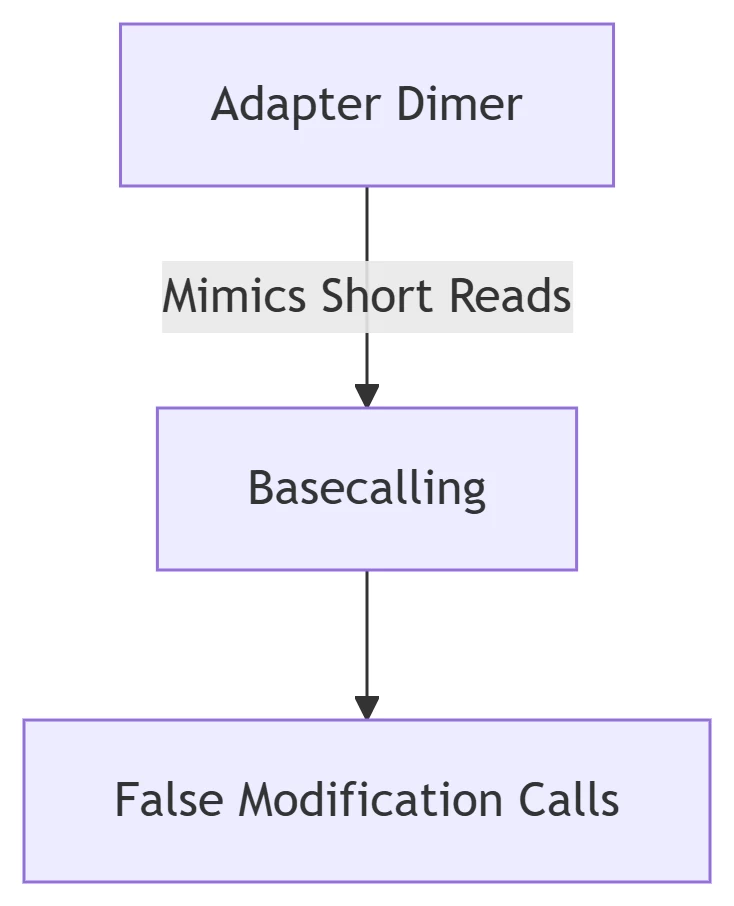
-
Identification: Bioanalyzer peak ~120-150 bp
-
Prevention:
-
AMPure XP bead cleanup (0.6x ratio)
-
Reduce adapter concentration by 25%
-
B. Incomplete PolyA Selection
-
Manifestations:
-
20% rRNA reads in sequencing
-
Erroneous tRNA/lncRNA modification calls
-
-
Optimization:
-
Double PolyA+ selection for challenging samples
-
RNA CS spike-in validation
-
3. Sequencing Configuration Errors
A. Flow Cell Degradation
-
Warning Signs:
-
Pore occupancy <70%
-
Current noise SD >1.2 pA
-
-
Preventive Protocol:
New Flow Cell
Pre-run Wash
Proper Priming
4°C Hydrated Storage
B. Suboptimal Run Parameters
| Parameter | Error | Correction |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage | >200 mV | Set to 140-180 mV |
| Run Time | <48 hours | Extend to 72 hours |
| Basecaller Config | DNA config for RNA | Use rna_r10.4.1_e8.2_hac |
4. Computational Processing Mistakes
A. Basecalling Inaccuracies
-
Problematic Outcomes:
-
Homopolymer misreads (e.g., AAAAA → AAAA)
-
Indels in modification-rich regions
-
-
Resolution:
# Upgrade command guppy_basecaller --config rna_r10.4.1_e8.2_400bps_sup.cfg --device cuda:0
B. Reference Genome Mismatch
-
Error Signature: Alignment rate <70%
-
Validation Protocol:
-
Confirm assembly version (e.g., GRCh38 vs. T2T-CHM13)
-
Use
minimap2 -ax splice -uf -k14for splicing
-
5. RNAmod Analysis Missteps
A. Inadequate Parameter Thresholding
| Parameter | Error Value | Optimal Value | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Confidence Threshold | <0.75 | ≥0.85 | 40% false positives |
| Min Coverage | <10x | ≥20x | Low reproducibility |
B. GPU Underutilization
-
Symptom: Runtime >48 hours for 100M reads
-
Solution:
tandemmod predict --gpu 1 --batch_size 256
6. Validation and Quality Control Failures
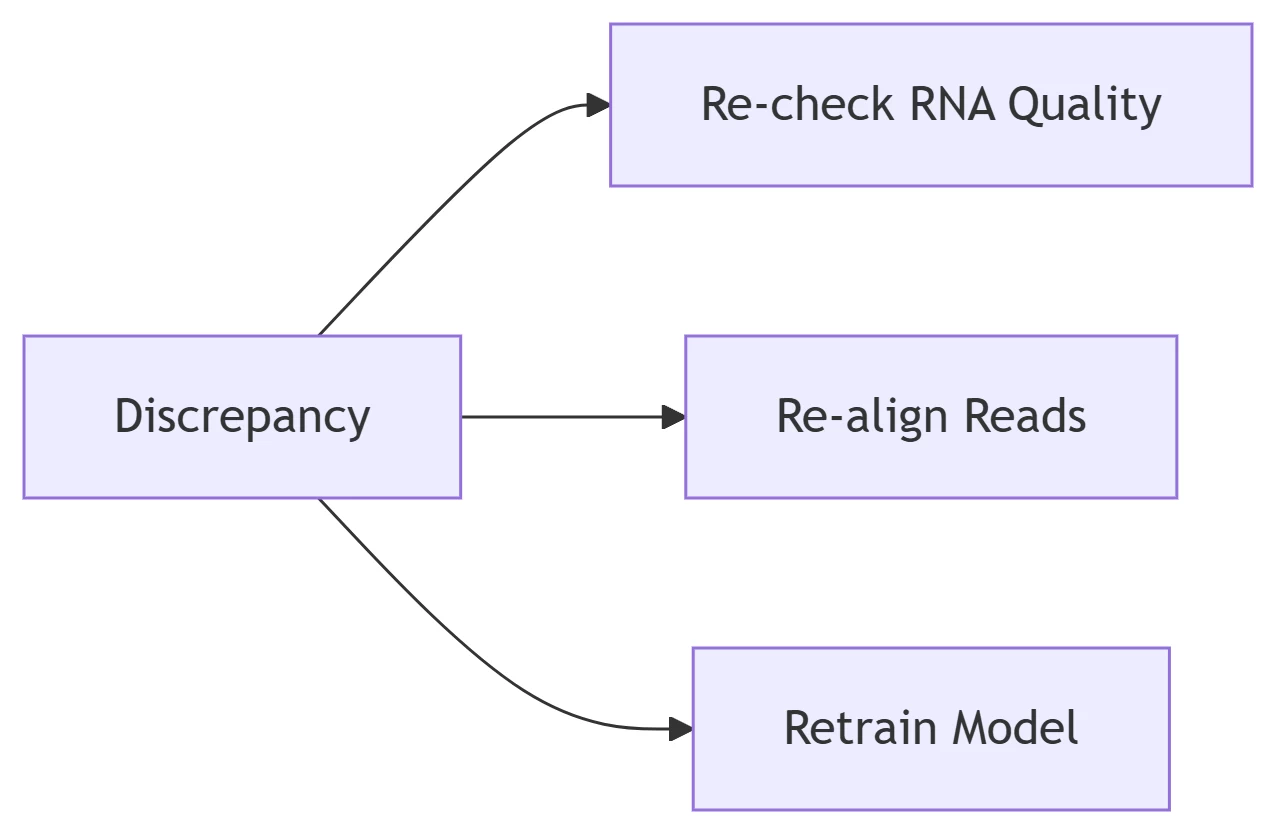
A. Orthogonal Method Discrepancies
-
Common Scenario:
-
RNAmod m⁶A calls vs. miCLIP show <80% concordance
-
-
Resolution Framework:
B. Inadequate Controls
-
Essential Controls:
-
IVET synthetic RNA with known modifications
-
Biological replicates (n≥3)
-
Knockout cell lines (e.g., METTL3-KO)
-
7. Troubleshooting Flowchart
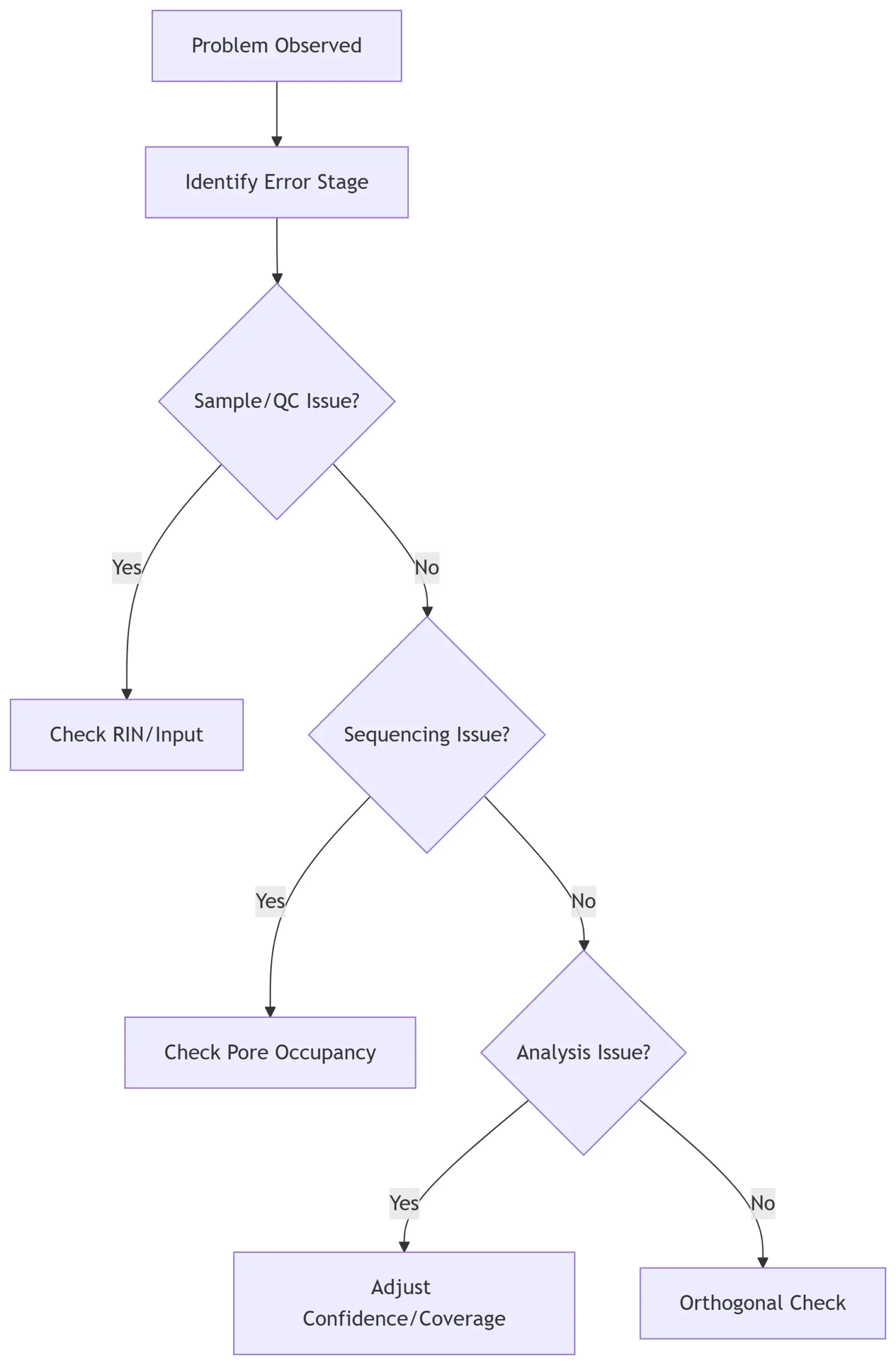
Conclusion
The most frequent RNAmod errors stem from:
-
Sample Degradation: Prevent by RIN verification and aliquotting
-
Adapter Artifacts: Eliminate via bead cleanup optimization
-
Computational Oversights: Fix through parameter tuning (confidence ≥0.85, coverage ≥20x)
-
Validation Gaps: Resolve with IVET controls and orthogonal methods
Proactive monitoring at each workflow stage—coupled with GPU acceleration and species-specific model retraining—reduces error rates by >60%. These protocols ensure high-fidelity detection of m⁶A, m⁵C, and Ψ modifications for disease research and therapeutic development.
Data sourced from public references. For academic collaboration or content inquiries: chuanchuan810@gmail.com
-
